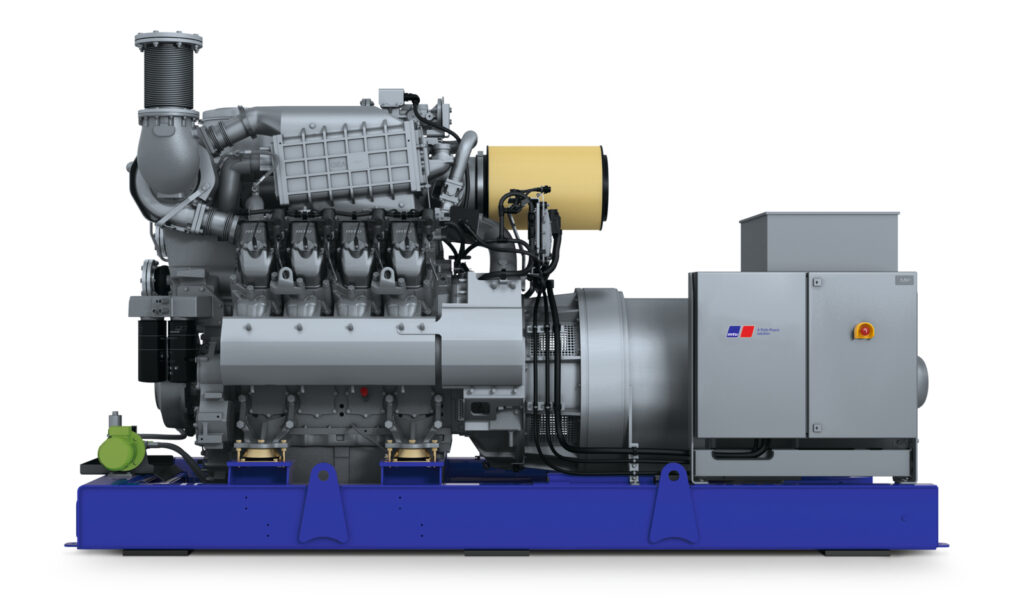
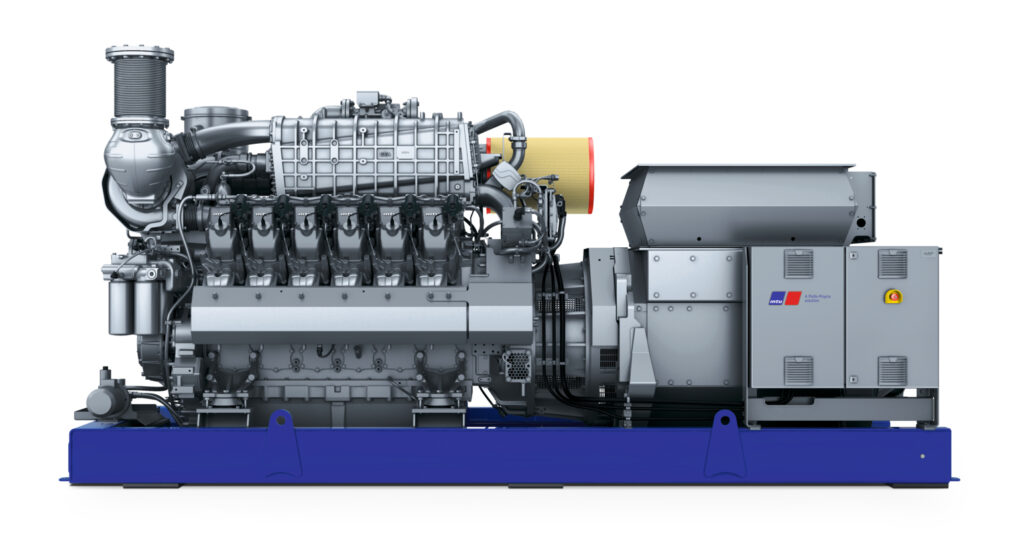
Trigeneration (Combined Heat, Power and Cooling) is the combined production of heat, power and consumable cooling in a single process, which allows for a reduction in the amount and cost of primary energy required to produce each of the above separately. Combined heat, power and cooling (CHPC) is the technological successor to combined heat and power (CHP), which enables the generation of electricity and waste heat in a single process. Trigeneration extends the potential of CHP with an additional type of energy – consumable cold – which can be used, for example, in air conditioning or production processes.
As Trigeneration is a great way to improve the cost-effectiveness of electricity generation in district heating systems and balance the demand for electricity and heat, it prevents potential blackouts during hot weather.
A CHPC system is made up of a CHP module producing electricity and waste heat, which in turn is used by an absorption unit to produce cooling.
Application:
Trigeneration is beneficial for units requiring three types of energy simultaneously (for example, in hospitals, data centres). Tri-generation allows electricity and heat demand to be balanced during the summertime and consequently prevents a potential collapse in electricity supply on hot days.